Inline vs inline-block Display in CSS
Posted on: August 26, 2020 by Amilcar Paco
In this article, we will see the difference between Inline vs. inline-block
The display property defines how the components are going to be placed on the web page.
Contents
Syntax
display: value;Inline-block
- Allows setting a width and height on the element.
- The top and bottom margins/paddings are respected.
- Does not add a line-break after the element, so the element can sit next to other elements.
- It is used to display an element as an inline-level block container.
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Inline vs Inline-block</title>
<style>
html, body {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.menu{
list-style-type: none;
text-align: center;
background-color: red;
}
.menu li {
display: inline-block;
padding: 25px;
font-size: 25px;
}
span {
display: inline-block;
width: 100px;
background-color: blue;;
height: 100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Menu Bar - with inline-block</h1>
<ul class="menu">
<li>Home</li>
<li>Services</li>
<li>About Us</li>
<li>Contact Us</li>
</ul>
<p>This is a simple <span>text</span> with inline-block.</p>
</body>
</html>Output

Inline
- It is used to displays an element as an inline element.
- An inline element does not start on a new line and only takes up as much width as necessary.
- Any height and width properties will have no effect.
Example
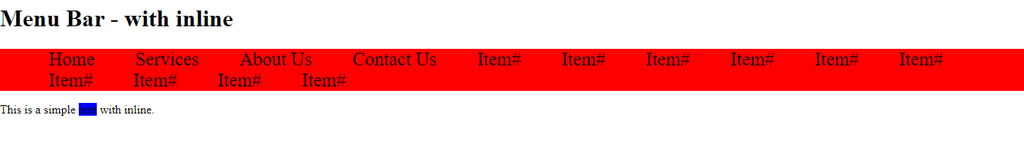
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Inline vs Inline-block</title>
<style>
html, body {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.menu{
list-style-type: none;
background-color: red;
}
.menu li {
display: inline;
padding: 25px;
font-size: 25px;
}
span {
display: inline;
width: 100px;/* won't have any effect */
background-color: blue;;
height: 100px; /* won't have any effect */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Menu Bar - with inline</h1>
<ul class="menu">
<li>Home</li>
<li>Services</li>
<li>About Us</li>
<li>Contact Us</li>
<li>Item#</li>
<li>Item#</li>
<li>Item#</li>
<li>Item#</li>
<li>Item#</li>
<li>Item#</li>
<li>Item#</li>
<li>Item#</li>
<li>Item#</li>
<li>Item#</li>
</ul>
<p>This is a simple <span>text</span> with block.</p>
</body>
</html>Output
Conclusion
You can use it to set whether an element is treated as a block or inline part and the layout used for its children, such as flow layout, grid, or flex.
Thanks for reading!
Share on social media
//